Siberia’s mysterious landscape is once again in the spotlight, this time because of the ever-expanding Batagaika Crater, which resembles a giant gateway to the underworld. First formed in 1991 when a hillside collapsed, this crater has continued to grow in the northern Yakutia region’s Yana Uplands. Since then, it has been a cause for concern among researchers, as it reveals the impact of global warming in a dramatic way. Here’s why this crater is making scientists anxious.
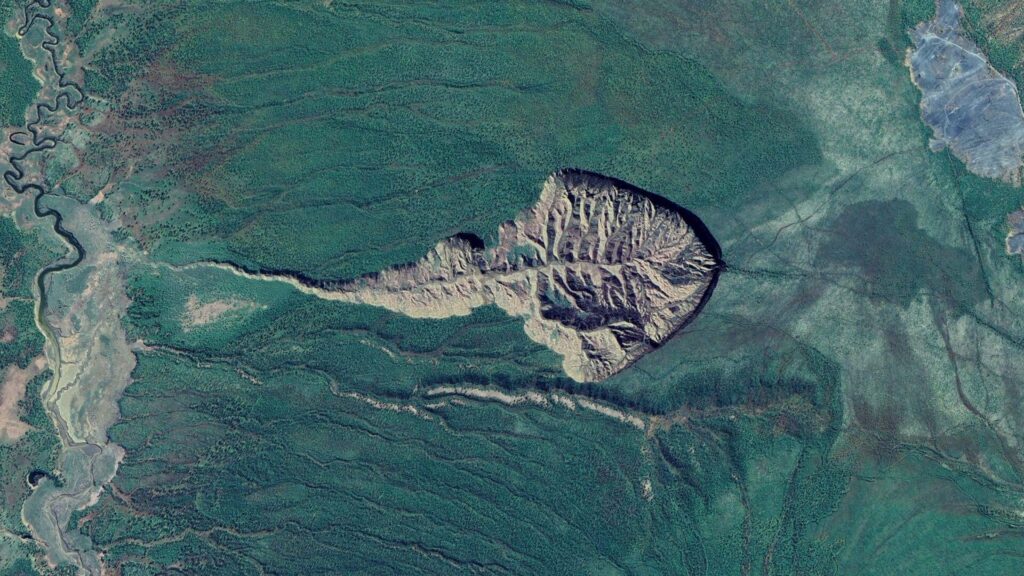
The Rapid Expansion of Batagaika Crater
The Batagaika Crater expands by approximately 1 million cubic meters every year, exposing one of the world’s oldest permafrost layers. The primary reason for the crater’s continuous growth is the melting of the surrounding permafrost. As the walls of the crater erode due to thawing soil, the crater’s size increases, setting off a chain reaction.
As the Batagaika Crater grows, it accelerates the melting of permafrost, which, in turn, causes further erosion. Scientists worry that if the crater continues to expand at this rate, the surrounding permafrost will melt even faster, leading to severe environmental consequences.
Global Warming and Its Far-Reaching Effects
The rapid growth of the Batagaika Crater is not just about its physical size; it also highlights the profound effects of global warming. Rising temperatures are melting deeper layers of permafrost, releasing ancient gases and microorganisms into the atmosphere. Among the most surprising discoveries is the revival of a 40,000-year-old “zombie virus” that had been frozen in the permafrost.
One of the factors contributing to the crater’
New Scientific Insights
Recen
The Batagaika Crater, a massive gash in Siberia’s landscape, serves as a stark reminder of the power of nature and the consequences of human influence. This “gateway to the underworld” might also offer a glimpse into Earth’s hidden secrets, as it continues to grow and reveal layers of ancient history.

