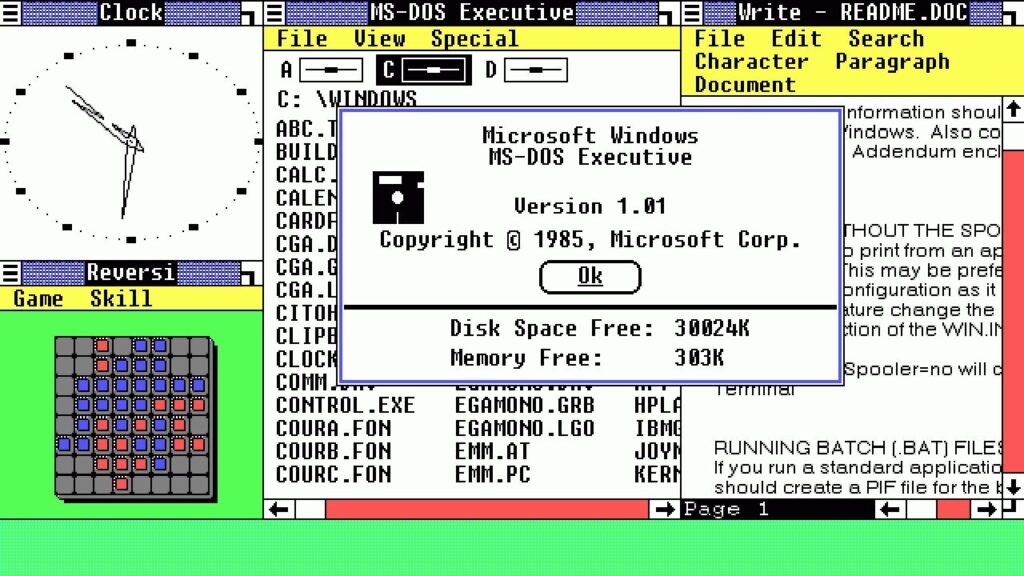
The Dawn of Windows: 1985
On November 20, 1985, Microsoft made a groundbreaking move that would change the landscape of personal computing forever. This was the year Windows 1.0 was introduced. Sold for $100, it offered features like Paint, Notepad, and, crucially, mouse support, which was a significant departure from the keyboard-only control of previous computers. However, despite its innovative features, Windows 1.0 did not achieve significant commercial success.
Windows 2: 1987
Two years later, Windows 2.0 hit the market. This version brought the ability to overlap windows, create icons, and zoom in and out. It also introduced the first versions of Microsoft Word and Excel, laying the foundation for the productivity suite we know today.
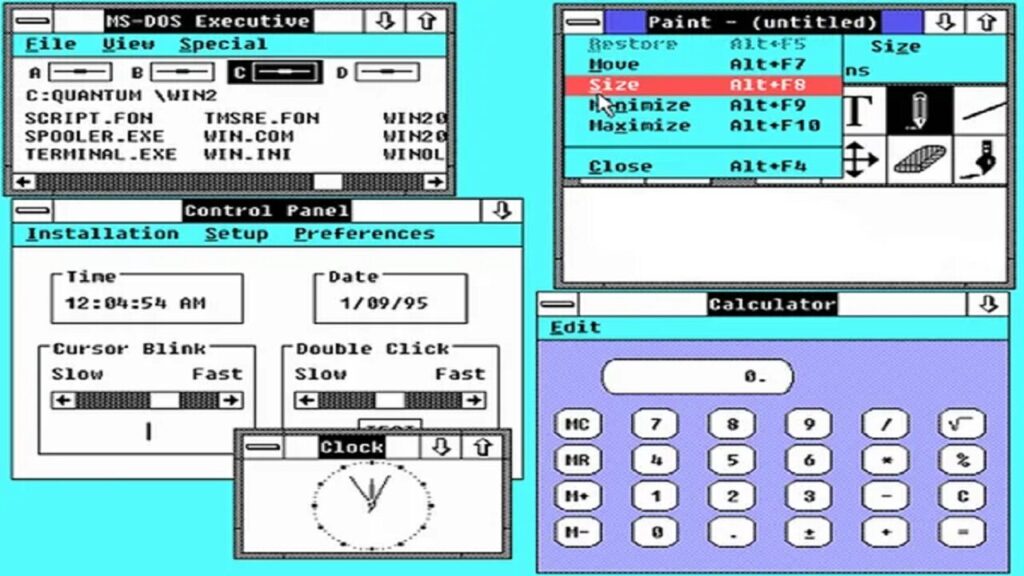
Windows 3: 1990
By 1990, Microsoft released Windows 3.0, which offered a more advanced interface and became a strong competitor to Apple Macintosh and Commodore Amiga. This version introduced the beloved Minesweeper game in its subsequent update, Windows 3.1.
Windows 95: 1995
1995 saw the launch of Windows 95, a significant leap forward with the introduction of the Start button. This 32-bit operating system brought features like the desktop, right-click functionality, Internet Explorer, USB support, and Plug-and-Play capabilities.
Windows 98: 1998
Windows 98 followed, enhancing the user experience with Outlook Express, Windows Address Book, Microsoft Chat, and NetShow Player. It also provided better support for software developers.
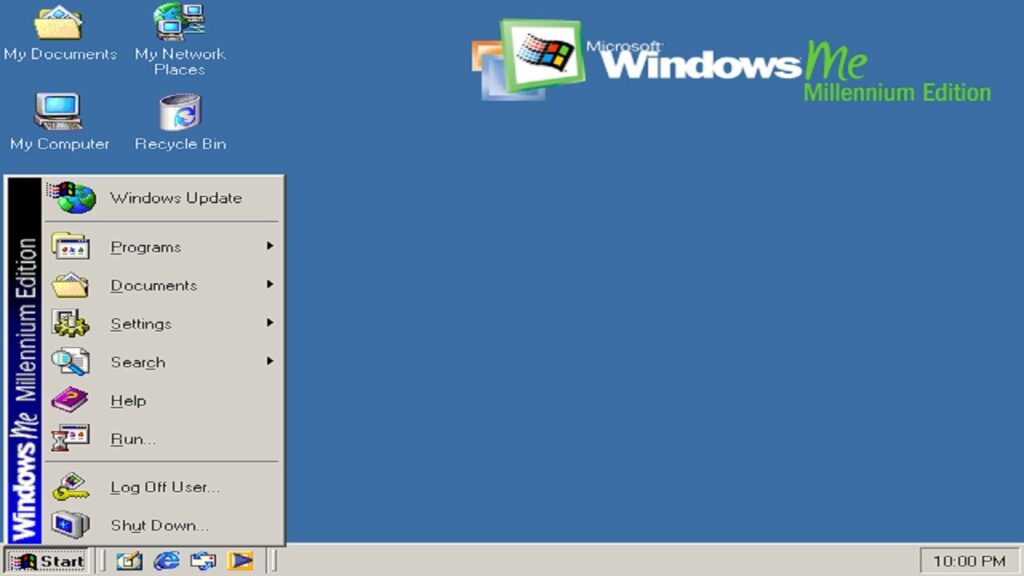
Windows ME: 2000
In 2000, Windows Millennium Edition (ME) was released. Despite its numerous system errors, it was tailored for home use and introduced Windows Movie Maker.
Windows XP: 2001
A pivotal release came in 2001 with Windows XP, which offered a modern design and features like remote access, user accounts, built-in CD burning, and ClearType. However, it faced significant security challenges.
Windows Vista: 2007
Windows Vista, released in 2007, was a major effort by Microsoft focusing on design and security. However, it failed due to performance issues and hardware compatibility problems.
Windows 7: 2009
Windows 7 arrived in 2009, successfully restoring Microsoft’s reputation with improved performance and user satisfaction. It became one of the most popular Windows versions.
Windows 8: 2012
In 2012, Windows 8 marked a dramatic shift by removing the Start button and menu, aiming for a more touch-friendly interface. However, this change was not well-received by users.
Windows 10: 2015
With Windows 10 in 2015, Microsoft returned to a more traditional desktop interface, reinstating the Start menu and refining the user experience based on previous feedback.
Windows 11: 2021
The latest iteration, Windows 11, was introduced in 2021, featuring a redesigned interface and several new functionalities to enhance the user experience.
Reflecting on Windows’ Evolution
From its humble beginnings in 1985 to its current form, Windows has continually evolved, introducing new features and adapting to the needs and feedback of its users. As we approach its 39th anniversary in 2024, it is clear that Windows has significantly shaped the world of personal computing.

