Scientists have discovered a new planet, Gliese-12b, which could potentially support human life. Located relatively close to Earth, Gliese-12b is about the same size as Venus and offers promising conditions that might sustain life.
Gliese-12b’s Potential for Habitability
- Proximity and Size: Gliese-12b is located within a close distance to Earth in cosmic terms and is similar in size to Venus, often referred to as Earth’s twin. This discovery could provide valuable insights into other Earth-like planets in the cosmos.
- Habitable Zone: The planet resides in the habitable zone of its host star, meaning it has the ideal conditions to possibly harbor liquid water on its surface. This crucial factor makes it a strong candidate for supporting life.
Discovery and Characteristics
- Detection Methods: Scientists detected Gliese-12b using NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) along with supporting data from other observatories. They calculated the planet’s size, temperature, and orbital characteristics.
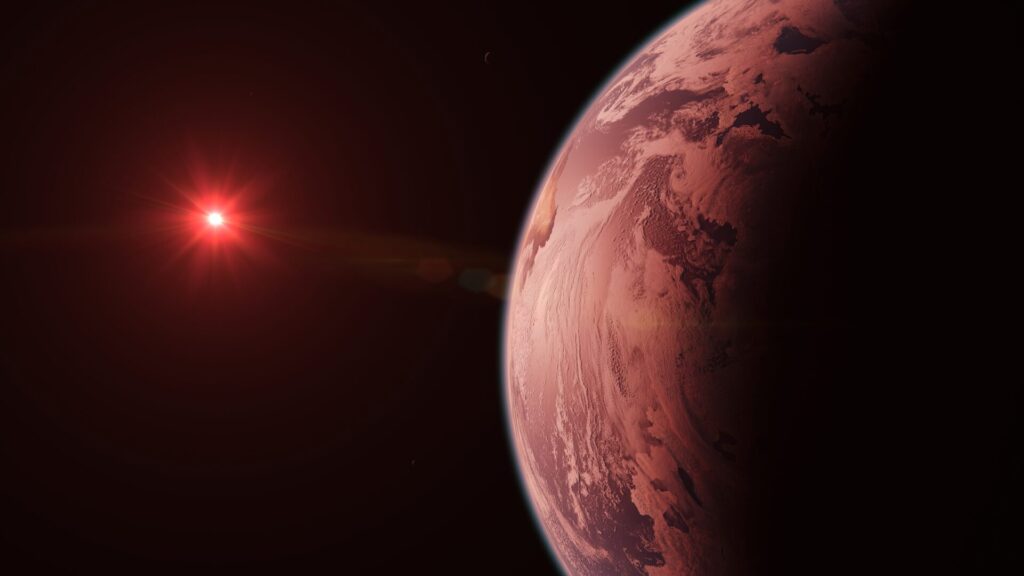
- Location: Gliese-12b orbits a cold red dwarf star known as Gliese 12, situated in the Pisces constellation, approximately 40 light-years away. While this is relatively close in space terms, it would still take around 300,000 years to reach with our fastest spacecraft.
- Temperature and Orbit: The average temperature on Gliese-12b is around 42°C, indicating potential habitability. Despite its close orbit of 12.8 days around its star, the cool red dwarf star Gliese 12, which is only 27% the size of our Sun and 60% as hot, provides a less intense heat environment.

Energy and Atmospheric Conditions
- Energy Reception: Data suggests that Gliese-12b receives about 1.6 times the energy from its star as Earth does from the Sun, equating to roughly 85% of the energy Venus receives. This indicates a warmer environment, but not excessively hot due to the star’s lower output.
- Atmospheric Uncertainty: Currently, it is unknown whether Gliese-12b possesses an atmosphere. This uncertainty makes the planet an excellent candidate for further study using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST).

Future Exploration
The next steps for researchers involve examining Gliese-12b’s atmosphere to determine if it shares similarities with Earth’s atmosphere. This will help assess its true potential for supporting life. Further investigation with advanced telescopes like JWST will provide deeper insights into this intriguing new world.

