Researchers have observed a near doubling of global measles cases from 2022 to 2023, presenting significant challenges to the ongoing efforts aimed at achieving and maintaining elimination status in numerous countries.
Dr. Patrick O’Connor of the World Health Organization (WHO) revealed alarming statistics at the ESCMID Global Congress in Barcelona. In 2022, there were 171,153 measles cases globally, but provisional data indicates a sharp increase to 321,582 cases in 2023. The numbers for 2024, although not finalized, are already substantia
Almost half of this year’s cases have been reported in the WHO European Region, with countries like Azerbaijan, Kyrgyzstan, and Yemen experiencing particularly high incidence rates.
Situation in the United States
The United States has also witnessed a concerning rise in measles cases, with 128 reported cases across 20 jurisdictions this year. This marks the highest count since 2019, posing a threat to the country’s previously achieved elimination status.
Health Risks and Complications
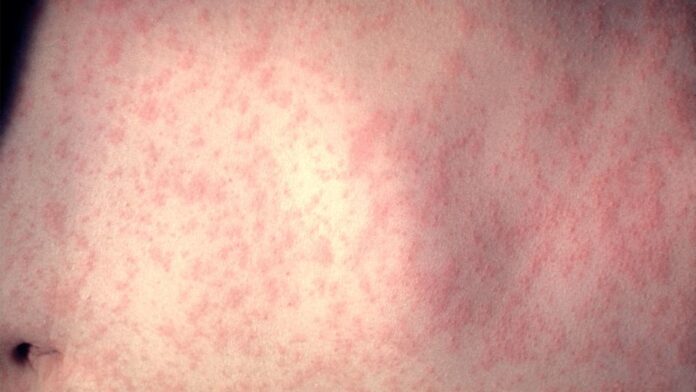
Measles, being highly contagious, poses severe health risks, especially to young and unvaccinated individuals. Symptoms include fever, cough, runny nose, watery eyes, and a characteristic rash. Complications such as pneumonia and encephalitis can occur, with potential fatal outcomes.
Impact of Measles Vaccination
Despite the challenges, measles vaccination has been instrumental in preventing an estimated 57 million deaths between 2000 and 2022, highlighting the importance of vaccination efforts.
In the United States, the CDC recommends children receive the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine, with the first dose administered between 12 and 15 months of age, followed by a second dose between 4 and 6 years old. The vaccine has shown high effectiveness, significantly reducing the risk of measles infection.
However, vaccination coverage has fallen below target levels in recent years, with only 93.1% of kindergarteners completing their MMR vaccine series in the 2022-23 school year.
Addressing the Crisis
Measles outbreaks are particularly prevalent in conflict-affected and fragile countries, underscoring the urgent need for high and equitable routine immunization coverage, coupled with rapid outbreak response measures.
The surge in global measles cases highlights the ongoing challenges in disease control efforts and underscores the critical importance of vaccination programs in combating the spread of this highly contagious disease.