As El Niño comes to an end, scientists are now turning their attention to what the future holds in terms of climate patterns. While the conclusion of this weather phenomenon brings relief in terms of the extreme weather events it often brings, there is still uncertainty about what comes next. The cooling of the Pacific Ocean is a positive sign, as it indicates a return to more normal conditions. However, the question remains whether this return to normalcy will be short-lived or if it marks the beginning of a new phase in the climate system.
Climate change continues to be a pressing concern, with the El Niño event exacerbating its effects. The warming of the Pacific Ocean during El Niño contributed to the overall rise in global temperatures, highlighting the interconnectedness of natural climate variability and human-induced climate change. While El Niño is a naturally occurring phenomenon, its impacts are amplified by the warming planet. As such, understanding the future trajectory of climate patterns is crucial in order to effectively mitigate and adapt to the challenges posed by climate change.
Scientists are now closely monitoring the Pacific Ocean and other key climate indicators to gain insights into what lies ahead. One area of focus is the possibility of a La Niña event, which often follows an El Niño. La Niña is characterized by cooler-than-normal sea surface temperatures in the equatorial Pacific and can have its own set of impacts on global weather patterns. It is uncertain whether a La Niña will develop and, if so, how strong it will be.
Furthermore, researchers are also studying the long-term trends in climate variability and the potential influence of climate change on these patterns. The warming planet is altering the dynamics of the climate system, making it increasingly difficult to separate natural variability from human-induced changes. This uncertainty poses challenges for predicting future climate patterns and understanding their implications for ecosystems, agriculture, and human societies.
Despite the uncertainty, one thing is clear: the need for action on climate change remains urgent. The conclusion of El Niño serves as a reminder of the complex and interconnected nature of our climate system. It underscores the importance of reducing greenhouse gas emissions, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and implementing strategies to adapt to the changing climate. By taking decisive action now, we can work towards a more sustainable and resilient future for generations to come.
Indications of Climate Change
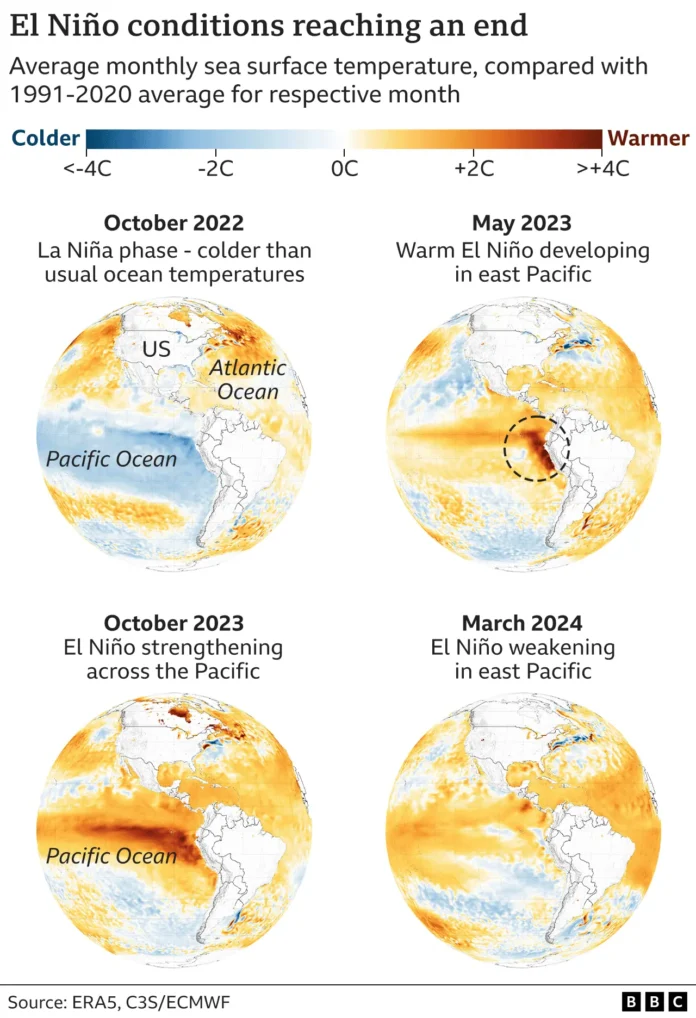
A string of recent global monthly high temperature records has raised concerns among scientists that the world could be entering a new phase of even faster climate change. The months following the end of El Niño will provide a strong indication as to whether the recent high temperatures are due to accelerated climate change or not. El Niño occurs every few years and brings dramatic changes to weather patterns in various parts of the world. The surge of warmer water off the coast of Peru in South America is linked to increased droughts and floods in different regions.
As scientists continue to study the impacts of climate change, they have identified several key indications that point towards its existence. One of the most significant indicators is the consistent breaking of global monthly high temperature records. Over the past few years, there has been a noticeable trend of these records being shattered, leading experts to believe that the planet is experiencing a rapid and unprecedented increase in temperatures.
The recent surge in high temperatures has raised concerns among scientists about the potential acceleration of climate change. While it is known that El Niño events occur cyclically every few years, the aftermath of these events can provide valuable insights into the long-term effects of climate change. As the current El Niño event comes to an end, scientists are closely monitoring the subsequent months to determine whether the recent high temperatures are solely attributed to the natural phenomenon or if they are indicative of a larger climate change pattern.
El Niño, characterized by the warming of the Pacific Ocean surface waters, has a profound impact on global weather patterns. Its effects are felt across different regions, leading to both droughts and floods in various parts of the world. The surge of warmer water off the coast of Peru in South America, for example, disrupts the normal atmospheric circulation, causing shifts in precipitation patterns. This can result in prolonged dry spells in some areas and excessive rainfall in others.
Understanding the link between El Niño and climate change is crucial in deciphering the true causes of the recent high temperatures. While El Niño events have occurred throughout history, the frequency and intensity of these events may be influenced by climate change. Scientists are working to unravel the complex relationship between El Niño and global warming, studying the long-term trends and potential feedback loops that may be exacerbating the effects of both phenomena.
In conclusion, the indications of climate change are becoming increasingly evident through the consistent breaking of global temperature records and the influence of El Niño events on weather patterns. The months following the conclusion of the current El Niño will provide valuable insights into the role of climate change in the recent high temperatures. As scientists continue their research, it is imperative that we recognize the urgency of addressing climate change and take necessary actions to mitigate its impacts on our planet.
Despite the differing opinions among scientists, there is a general consensus that the end of El Niño does not necessarily mean a return to normal conditions. The effects of this weather pattern are far-reaching and can have significant impacts on global weather patterns. For example, during an El Niño event, there is typically a decrease in the number of hurricanes in the Atlantic, while the Pacific experiences an increase in tropical cyclones.
One aspect that researchers are particularly interested in is the potential transition from El Niño to La Niña. La Niña is characterized by cooler-than-normal sea surface temperatures in the equatorial Pacific, which can have its own set of consequences. For instance, it can lead to increased rainfall in the western Pacific, while regions like Australia and parts of South America may experience drought conditions.
Understanding the future of ENSO is crucial for weather forecasting and climate prediction. It can provide valuable insights into the likelihood of extreme weather events such as heatwaves, droughts, and flooding. Additionally, it can help inform decision-making in sectors such as agriculture, water resource management, and disaster preparedness.
Given the complexity of ENSO and the multitude of factors that influence its behavior, scientists continue to study and monitor the Pacific Ocean and its surrounding regions. Advanced technologies such as satellite observations, ocean buoys, and climate models are utilized to gather data and make predictions about the future state of ENSO.
In conclusion, while the current El Niño has come to an end, the impacts of this weather phenomenon are far from over. The transition to La Niña or a return to neutral conditions will have its own set of consequences, which can vary depending on the region. As scientists strive to better understand and predict ENSO, it is important to remain cautious and recognize the uncertainties that exist in forecasting future weather patterns.
The Impact of La Niña
Whether or not a La Niña forms is of significant importance to researchers. It can have a substantial impact on storms and hurricanes, with some experts predicting that if La Niña does occur, it would lead to a highly active hurricane season in the Atlantic. Additionally, La Niña’s cooling effect may slightly slow the rate of global heating. This could suggest that the record temperatures experienced over the past year were somewhat of a mystery and not necessarily evidence of a more rapid phase of warming.
In conclusion, the end of El Niño has brought uncertainty about the future and its impact on climate change. The coming months will provide valuable insights into the causes of recent high temperatures and whether they are a result of accelerated climate change. The development of La Niña, if it occurs, could have significant effects on weather patterns and the rate of global heating. As scientists continue to monitor and study these phenomena, the world waits to see what lies ahead in the ongoing battle against climate change.
One of the key impacts of La Niña is its effect on precipitation patterns. While El Niño typically brings above-average rainfall to certain regions, La Niña tends to have the opposite effect, causing drier conditions in some areas. This can have serious implications for agriculture, water resources, and ecosystems. For example, regions that rely on regular rainfall for crop production may experience decreased yields and increased risk of drought during a La Niña event. On the other hand, regions that are prone to flooding during El Niño may experience relief during a La Niña phase.
Furthermore, La Niña can also influence global weather patterns, leading to changes in temperature and atmospheric circulation. In the Pacific Ocean, La Niña is associated with cooler sea surface temperatures, which can impact the formation and intensity of tropical cyclones. In the Atlantic, a La Niña event can lead to increased wind shear, which inhibits the development of hurricanes. However, it is important to note that while La Niña may reduce the overall number of hurricanes, it does not guarantee that any specific region will be spared from the impacts of a major storm.
Additionally, the cooling effect of La Niña on global temperatures can have implications for climate change. While the long-term trend of global warming is driven by human activities, natural climate phenomena like El Niño and La Niña can temporarily influence temperature patterns. The cooling effect of La Niña may provide a brief respite from the rapid warming observed in recent years. However, it is crucial to remember that this does not negate the need for urgent action to mitigate climate change. The underlying drivers of global warming, such as greenhouse gas emissions, must still be addressed to prevent further long-term climate disruptions.
In summary, the potential formation of La Niña has significant implications for weather patterns, precipitation, and global temperatures. Its effects on storms, hurricanes, and regional climate variability can have both positive and negative consequences for various sectors, including agriculture, water resources, and disaster management. While La Niña may temporarily slow the rate of global heating, it does not diminish the urgency of addressing climate change. As scientists and policymakers continue to monitor and study these phenomena, it is crucial to prioritize sustainable practices and reduce greenhouse gas emissions to ensure a stable and resilient future for our planet.