Australian-based electrolyzer manufacturer Hysata announced that it has developed the world’s most efficient electrolyzer with a 95% efficiency rate and is preparing to produce its new product on a large scale.
As countries strive to move away from fossil fuels, they are turning to different renewable energy sources. While sources like wind and solar are becoming increasingly common, they are intermittent and variable, requiring storage. Hydrogen becomes important in this regard. It can be produced and stored using excess electricity and used for various purposes.
While batteries stand out as a way to store electricity, factors such as high cost and low energy density prevent batteries from being the best option in all cases. Hydrogen, particularly due to its lightness, can be a good alternative for long-distance transportation and aviation. Moreover, it holds significant potential as a heat source in industries.
Efficiency Problem and Solution
Electrolyzers that split water to produce hydrogen have been available for a long time, but their efficiency remains low. According to Hysata’s website, the highest efficiency offered by current electrolyzers is approximately 75%. Using these electrolyzers to produce one kilogram of hydrogen requires 52.5 kWh of energy, and one kilogram of hydrogen can produce 39.4 kWh of energy under ideal conditions.

The latest electrolyzer design developed by Hysata achieves a 95% efficiency rate. In real-world terms, this means that only 41.5 kWh of energy is required to produce one kilogram of hydrogen.
Major Contribution to Efficiency
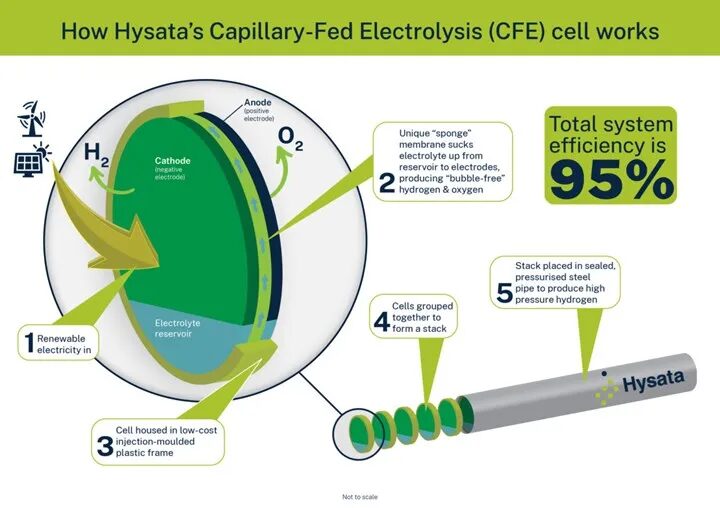
The most significant contribution to this achievement comes from research conducted by scientists at the University of Wollongong two years ago. At that time, scientists identified that bubbles in a traditional electrolyzer are resistant to the system and cause energy waste.
Bubbles are non-conductive and adhere to the electrode, preventing electrolyte from contacting the electrode and hindering efficient hydrogen splitting. To address this issue, a capillary-fed electrolyzer design was used to eliminate the bubbles.
In this setup, the electrolyte is placed at the bottom of the electrolyzer and drawn upward by a separator placed in the center and electrodes on both sides. The inner side of the electrode is in contact with the electrolyte, while the outer side turns into dry chambers where gas can collect.
This system significantly reduces resistance, and the electrolyte moves upward through capillary action. In laboratory tests, Hysata reported that the electrolyzer achieved 98% efficiency, with real-world conditions expected to achieve 95% efficiency.
The company is currently gearing up to increase the production capacity of these electrolyzers, which can be produced using materials abundant in the earth’s crust. Hysata says the technology is highly modular and can also be used to build facilities on a gigawatt scale.